Leave Your Message
In recent years, the growing demand for energy-efficient home heating solutions has brought Heat Pump Heaters into the spotlight. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can be more energy-efficient than traditional heating methods, reducing energy consumption by up to 50% in some cases. As the climate crisis intensifies, these systems are increasingly recognized for their potential to significantly lower carbon footprints while providing comfortable living environments.
Heat Pump Heaters operate on a simple principle: they transfer heat from one place to another, utilizing refrigeration technology. This not only makes them versatile for both heating and cooling applications but also enhances their appeal as a sustainable alternative to conventional fossil fuel-based heating systems. A recent report by the International Energy Agency indicates that integrating heat pumps into residential heating could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions by over 20% by 2030.
As homeowners seek innovative solutions to achieve energy independence and environmental sustainability, understanding the functionality and benefits of Heat Pump Heaters becomes crucial. This article will delve into the mechanics of how these systems work, their advantages, and considerations for homeowners looking to invest in an energy-efficient heating solution.

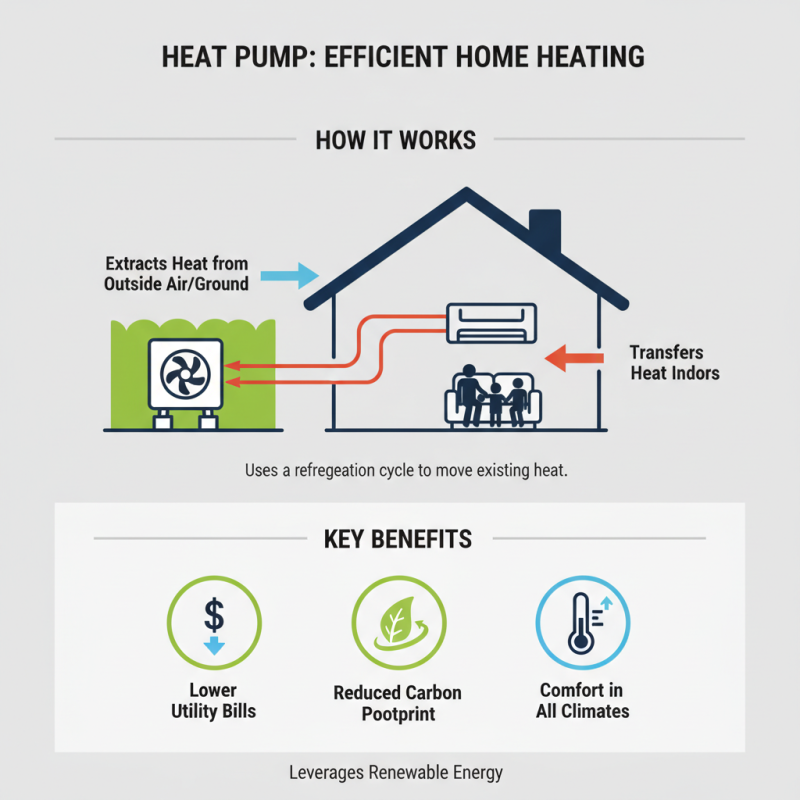
A heat pump heater is an innovative system designed to provide efficient home heating by transferring heat rather than generating it from scratch. Essentially, these systems utilize a refrigeration cycle to extract heat from the outside air, ground, or water and transfer it indoors. This process allows homes to stay warm even in colder climates. Unlike traditional heating systems that consume significant amounts of energy to create heat, heat pump heaters are known for their ability to leverage renewable energy sources, which can lead to lower utility bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
The operation of a heat pump heater revolves around a few key components: the compressor, evaporator, and condenser. During the heating process, the heat pump absorbs ambient heat and converts it into a gas. This gas is then compressed, dramatically increasing its temperature. The hot gas is sent to the condenser, where it releases heat into the home. After transferring its heat, the refrigerant returns to its liquid state, ready to start the cycle again. This method not only provides consistent warmth but also showcases the versatility of heat pumps, as they can typically reverse their operation in warmer months to function as air conditioners, making them a year-round climate control solution.
Heat pump heaters are becoming increasingly popular for residential heating due to their energy efficiency and eco-friendly operation. Understanding the types of heat pump heaters—air, ground, and water source—can help homeowners choose the best option for their heating needs.
Air source heat pumps are the most common type, extracting heat from the outside air, even in cold weather. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, modern air source heat pumps can reach efficiencies of up to 300%, meaning they can produce three times more energy than they consume. Ground source heat pumps, or geothermal pumps, leverage the stable temperatures of the earth to provide heating and cooling. They typically have higher upfront installation costs, but offer remarkable efficiency and lower operating costs over time, with performance ratings often exceeding 400%. Water source heat pumps operate similarly by extracting heat from a nearby water body, providing a consistent source of energy for thermal comfort.
Tips for homeowners considering a heat pump heater include evaluating local climate conditions, as extreme temperatures may affect performance. Additionally, assessing your home’s insulation and sealing air leaks can optimize the efficiency of any heat pump system. Investing in a professional installation is crucial to ensure the system operates correctly, maximizing both comfort and energy savings throughout its lifespan.
| Type of Heat Pump | Energy Source | Efficiency Rating (COP) | Typical Applications | Installation Costs (est.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Source Heat Pump | Air | 2.5 - 4.0 | Residential Heating/Cooling | $3,000 - $8,000 |
| Ground Source Heat Pump (Geothermal) | Ground | 3.0 - 5.0 | Whole Home Heating | $10,000 - $30,000 |
| Water Source Heat Pump | Water | 3.5 - 4.5 | Buildings Near Water Bodies | $5,000 - $15,000 |
Heat pump heaters are an innovative solution for home heating, using a unique process to extract warmth from the environment, even in cold temperatures. These systems operate on the principle of heat transfer; they draw heat from the air, ground, or water and move it indoors, providing efficient heating. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pump systems can be up to three times more efficient than traditional heating methods, converting one unit of electricity into up to three units of heat energy, significantly lowering energy bills and carbon emissions.
The mechanism behind heat pumps involves two primary components: an evaporator and a condenser. In colder months, these systems absorb low-temperature heat through the evaporator. A refrigerant circulates within the system, changing from liquid to gas as it takes in heat. This gas is then compressed, raising its temperature before it moves to the condenser, where the heat is released into the home. This cycle continues, providing consistent warmth while utilizing renewable energy from the environment.
Tips: When selecting a heat pump heater, consider additional features like smart thermostats that can optimize energy use. Regular maintenance, including checking refrigerant levels and cleaning filters, is crucial to ensure optimal performance and energy efficiency. For colder climates, opting for a dual-fuel system can enhance efficiency by integrating a backup heating source during extreme cold spells.
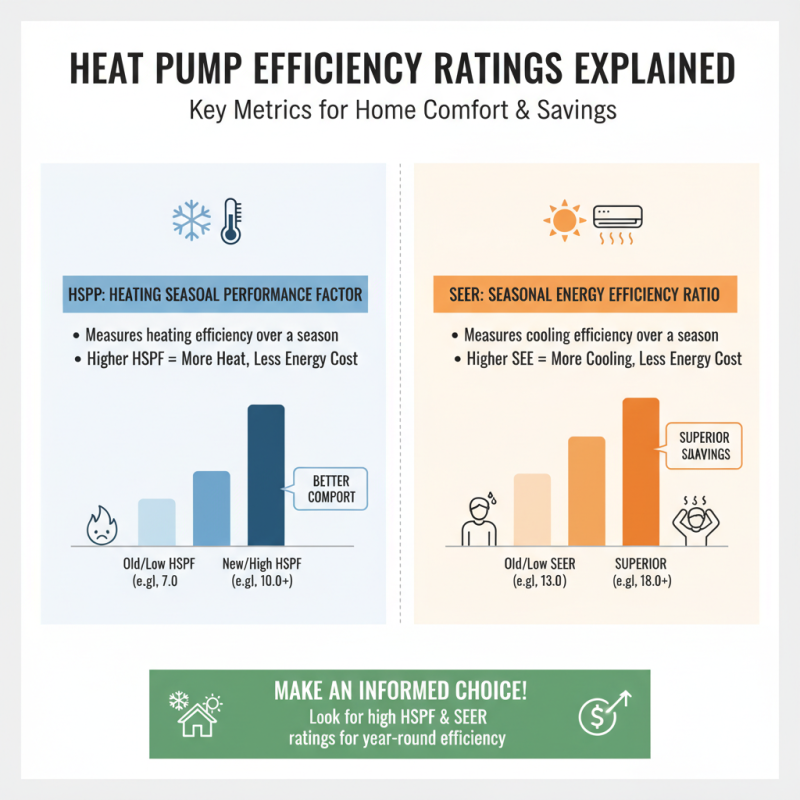
Understanding the efficiency ratings of heat pumps, particularly HSPF (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) and SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio), is crucial for making an informed choice for home heating. HSPF measures the efficiency of the heating mode, indicating how well a heat pump can convert electrical energy into heat over a heating season. A higher HSPF value signifies a more efficient unit, which translates to lower energy costs and increased comfort during colder months.
On the other hand, SEER evaluates the cooling efficiency of heat pumps, showing how effectively the unit uses electricity to provide cooling over a cooling season. Similar to HSPF, a higher SEER rating indicates a more efficient heat pump. Homeowners should look for units that offer a balance between high HSPF and SEER ratings, as this generally suggests better overall performance and efficiency year-round.
**Tips:** When selecting a heat pump, consider local climate conditions, as well as your home size and insulation quality, to determine the most suitable model. Additionally, regular maintenance can help maintain efficiency, so plan for periodic checks and servicing to ensure optimal performance.
Heat pump heaters are becoming increasingly popular for home heating due to their energy efficiency and versatility. These systems work by transferring heat from one place to another, using refrigerant to absorb heat from the outside air, ground, or water, even in cold temperatures. This process not only provides effective heating but can also be reversed to cool your home in the summer, making it a two-in-one solution for climate control.
Common applications of heat pump heating systems include residential homes, commercial buildings, and even in swimming pools. Homeowners appreciate the benefits of lower energy bills, as heat pumps use significantly less electricity compared to traditional heating systems like furnaces or electric heaters. Additionally, since heat pumps can operate efficiently across various climates, they are a viable option in many regions, promoting sustainability by reducing fossil fuel dependency.
Tips: For optimal performance, consider having your heat pump heater professionally installed to ensure proper sizing and efficiency. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning the filters and checking the refrigerant levels, can also extend the lifespan of your system and keep it running smoothly. Moreover, investing in a smart thermostat can further optimize energy use by allowing you to program heating schedules according to your lifestyle.






