Leave Your Message
When it comes to selecting an energy-efficient heating and cooling solution for your home, the right Heat Pump can make all the difference. According to Dr. Mark Thompson, a leading expert in the HVAC field, "Investing in the right heat pump is not just about comfort; it’s about maximizing efficiency and ensuring sustainability." With an increasing focus on reducing energy consumption and environmental impact, homeowners are recognizing the importance of making informed decisions.
Choosing the proper Heat Pump involves evaluating various factors including the size of your home, climate conditions, and energy source preferences. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in determining the efficiency and effectiveness of the heat pump you select. As Dr. Thompson suggests, understanding your specific needs and the available options will empower you to choose a heat pump that not only meets your comfort levels but also contributes to a greener future. This guide aims to provide you with essential tips that simplify the selection process, ensuring you make a confident and informed choice for your home heating and cooling needs.

When selecting a heat pump for your home, understanding the various types available on the market is crucial. The most common categories include air-source, ground-source (or geothermal), and water-source heat pumps. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, air-source heat pumps account for a significant portion of the market due to their efficiency and relatively lower installation costs. These systems transfer heat between the indoor air and the outdoors, making them an excellent choice for moderate climates. They typically have a seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) ranging from 14 to 20, which provides a clearer picture of their operational efficiency throughout different seasons.
On the other hand, ground-source heat pumps, which leverage the relatively stable temperatures of the ground, are often more efficient in extreme climates. A study published by the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE) indicated that geothermal heat pumps can achieve efficiencies of 400% or more in ideal conditions. Although the upfront installation costs are generally higher, the long-term savings on energy bills and their lower environmental impact often justify the investment.
Water-source heat pumps, which utilize nearby bodies of water, can also be an efficient option but are less common due to their limited geographical applicability. Understanding these options and their specific advantages can help homeowners make informed decisions tailored to their individual energy needs and environmental considerations.
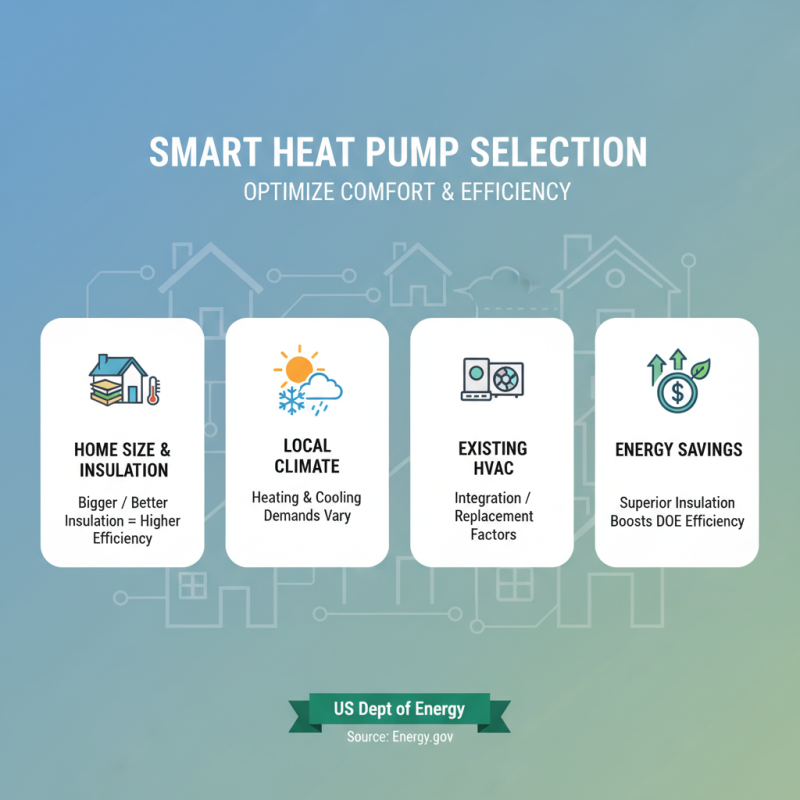
When considering a heat pump for your home, evaluating your heating and cooling needs is paramount. A comprehensive assessment should include your home’s size, insulation quality, local climate, and existing HVAC systems. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, homes with superior insulation can enhance the efficiency of heat pumps, enabling them to perform better with lower energy consumption. By understanding your home’s specific requirements, you can select a heat pump that not only meets your needs but also operates efficiently throughout the year.
One essential tip is to consider the appropriate capacity of the heat pump. Oversized systems can lead to short cycling, resulting in increased wear and tear as well as poor humidity control. Conversely, undersized units will struggle to maintain desired temperatures, leading to discomfort and higher energy bills. The Air Conditioning Contractors of America recommends calculating the heating and cooling loads of your home using Manual J calculation, which takes into account factors like square footage, window size, and insulation levels.
Another key consideration is the efficiency rating of the heat pump. The seasonal energy efficiency ratio (SEER) and heating seasonal performance factor (HSPF) are crucial metrics to gauge how well the system can convert energy into heating and cooling output. A higher SEER and HSPF indicate greater efficiency, which can significantly reduce energy costs over time. Energy Star reports that selecting a heat pump with a SEER rating of 15 or higher can yield substantial savings and environmental benefits, ultimately leading to a more comfortable and cost-effective home environment.
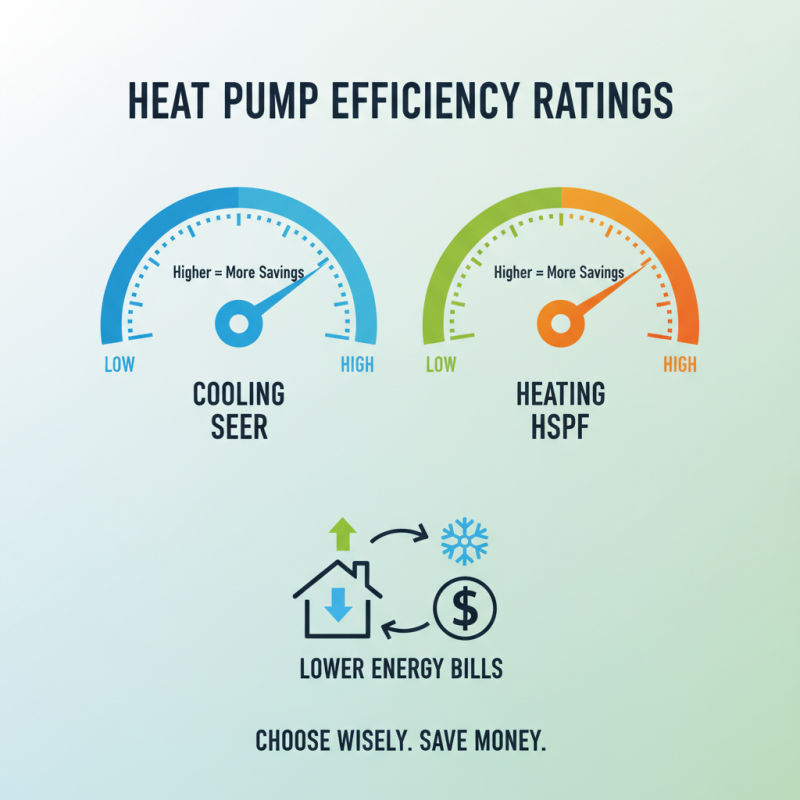
When evaluating heat pumps for your home, understanding energy efficiency ratings is crucial. These ratings, often expressed as the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) for cooling and the Heating Season Performance Factor (HSPF) for heating, can provide insight into the pump's performance and long-term operational costs. A higher SEER or HSPF indicates better efficiency, which translates to lower energy bills over time. It’s essential to choose a model that not only meets your heating and cooling needs but also fits within your budget by minimizing energy consumption.
Cost is another significant factor when selecting a heat pump. While upfront expenses can vary widely based on model and installation complexities, it’s essential to consider long-term savings. High-efficiency models may require a larger initial investment but often lead to considerable savings on utility bills. Additionally, look into potential rebates or incentives available for energy-efficient home improvements, as these can help offset the initial costs. Careful consideration of both energy efficiency ratings and overall costs will ensure you select the best heat pump that aligns with your home's requirements and budgetary constraints.
When choosing the right heat pump for your home, the installation space and location can significantly affect its performance and efficiency. It's crucial to ensure that there is adequate space for air circulation, allowing the unit to operate effectively. According to the Department of Energy, proper placement can enhance efficiency by as much as 20%. When considering the installation area, ensure that it's free from obstructions and debris, which can hinder the unit's performance.
Additionally, think about the environment where the heat pump will be installed. Research from the Energy Efficiency Council indicates that heat pumps perform best in moderate climates. Therefore, areas with extreme temperatures may require specialized models or configurations. It is also essential to position the heat pump away from direct sunlight or heavy wind, as these can adversely impact its efficiency.
**Tip**: Consult with a professional installer to assess your space and provide guidance on the ideal location for ductless or central systems.
Remember to factor in noise levels as well. Many units generate sound during operation, and installing them in a location away from bedrooms or common living spaces can enhance comfort.
**Tip**: Check the unit’s decibel ratings and select a model designed for quieter operation if noise is a concern in your residential layout.
| Tip | Description | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Assess Your Home's Size | Determine the square footage to select an appropriately sized heat pump. | Efficiency & Space |
| 2. Check Climate Requirements | Consider the temperature range in your area, as some units perform better in specific climates. | Performance |
| 3. Installation Space | Ensure you have enough space for the indoor and outdoor units, including airflow clearance. | Installation |
| 4. Energy Efficiency Ratings | Look for models with high SEER and HSPF ratings to save on energy costs. | Cost Savings |
| 5. Maintenance Requirements | Choose a heat pump that offers easy access for routine maintenance. | Longevity |
| 6. Smart Technology Integration | Consider models that can integrate with smart home systems for better control. | Convenience |
| 7. Noise Levels | Check the decibel rating to ensure the unit won’t be disturbingly loud. | Comfort |
| 8. Warranty Coverage | Review warranty options to protect your investment and future expenses. | Protection |
| 9. Professional Installation | Hire qualified professionals to ensure proper installation and efficiency. | Reliability |
| 10. Cost of Ownership | Consider both the initial purchase price and long-term energy costs. | Affordability |
When selecting a heat pump for your home, understanding the maintenance requirements and longevity is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. Research shows that regular maintenance can enhance the lifespan of a heat pump significantly. According to the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), a well-maintained heat pump can last between 15 to 20 years, while neglecting routine care can reduce this lifespan by as much as 50%. This underscores the importance of scheduling annual inspections and cleaning to avoid costly repairs and premature replacement.
In addition to regular maintenance, knowing the operational factors that affect a heat pump's longevity is essential. For instance, the climate in which the heat pump operates plays a significant role in its durability. The U.S. Department of Energy reports that heat pumps can lose efficiency in extreme temperatures; hence models designed for specific climatic conditions generally perform better and last longer. Moreover, keeping the surrounding area clear of debris and ensuring proper airflow can greatly enhance the efficiency and lifespan of a heat pump, leading to reduced energy costs and improved indoor comfort. Understanding these aspects is key to making an informed decision and ensuring your investment stands the test of time.
This chart illustrates the important factors to consider when choosing a heat pump for your home. Each factor is rated on a scale from 0 to 10, highlighting key aspects such as efficiency, cost, warranty, maintenance, and noise level.