Leave Your Message
In recent years, the demand for sustainable and energy-saving solutions has led to a significant focus on the development and implementation of Energy Efficient Heat Pumps. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can reduce energy consumption for heating and cooling by approximately 30% to 40% compared to traditional heating systems. This dramatic energy saving not only helps homeowners lower utility bills but also contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions, making them a pivotal technology for achieving climate goals.
Experts in the field, like Dr. Emily Johnson, a leading authority on renewable energy solutions, emphasize the importance of adopting Energy Efficient Heat Pumps in modern residential and commercial buildings. She stated, “The transition to energy-efficient technologies like heat pumps is essential for a sustainable future, as they enhance energy efficiency while providing reliable comfort.” As the global community pushes toward reducing carbon footprints, understanding how energy-efficient heat pumps operate and their benefits becomes increasingly vital.
Energy Efficient Heat Pumps work by transferring heat, utilizing a refrigeration cycle that can both warm and cool spaces effectively. This dual functionality, combined with advancements in technology, makes them a desirable option for reducing overall energy dependency. As we delve deeper into the mechanics and advantages of these systems, it is important to recognize their role in shaping a more energy-conscious world.

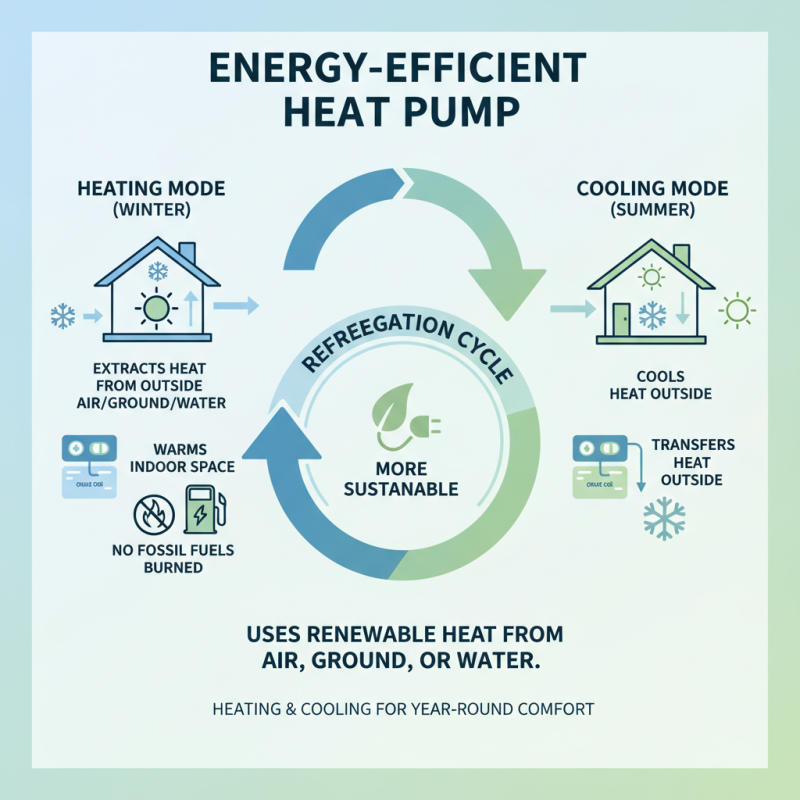
An energy efficient heat pump is a device designed to transfer heat from one location to another using a refrigeration cycle. Unlike traditional heating systems that generate heat by burning fossil fuels, heat pumps are capable of moving heat, making them a more sustainable option for heating and cooling spaces. They extract heat from the air, ground, or water, depending on the type of heat pump, and utilize this natural heat to warm a building during colder months or cool it in warmer months.
The efficiency of a heat pump is measured using its coefficient of performance (COP), which indicates how much heating or cooling is produced per unit of energy consumed. Modern energy efficient heat pumps utilize advanced technology to maximize energy transfer and minimize energy loss, allowing them to operate effectively even in extreme weather conditions. By utilizing renewable heat sources and consuming less electricity compared to conventional systems, these heat pumps not only reduce energy bills but also lower carbon footprints, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly environment.
Heat pumps are sophisticated systems that provide both heating and cooling by transferring heat from one area to another. The main components that contribute to the efficiency and functionality of heat pumps include the compressor, evaporator, condenser, and expansion valve. Each of these components plays a crucial role in facilitating the heat exchange process, ultimately resulting in an energy-efficient solution for climate control in residential and commercial settings.
The compressor is the heart of the heat pump, pressurizing the refrigerant and enabling it to absorb and release heat effectively. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, modern heat pumps can deliver up to three times more heat energy than the electrical energy consumed, a testament to the efficiency enabled by these core components. The evaporator absorbs ambient heat, even in colder temperatures, while the condenser releases this heat into the building. The expansion valve regulates the flow of refrigerant, ensuring optimal operation of the system.
Recent studies indicate that homes equipped with energy-efficient heat pumps consume approximately 50% less electricity for heating compared to traditional heating systems, significantly reducing energy bills and environmental impact. The integration of advanced technologies, such as variable-speed compressors and smart thermostats, further enhances the performance and efficiency of these systems. Understanding the key components of heat pumps and their functions is essential for maximizing their benefits in sustainable energy solutions.
Heat pump technology operates on the principles of thermodynamics, using a refrigerant to absorb and release heat energy efficiently. By moving heat from one location to another, heat pumps can provide both heating and cooling solutions while consuming significantly less energy than traditional heating systems. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, modern heat pumps can achieve efficiencies of up to 300% in ideal conditions, meaning they can produce three units of heat for every unit of electricity consumed. This remarkable energy transfer capability is primarily attributed to the heat pump’s ability to exploit the latent energy present in the environment.
The science behind heat pumps revolves around the refrigeration cycle, which consists of evaporation, compression, condensation, and expansion. During evaporation, the refrigerant absorbs heat from the surroundings (even in cold weather) and then is compressed, raising its temperature and pressure. The hot refrigerant gas then flows into the condenser, where it releases its stored heat into the indoor space before returning to the expansion valve. This efficient cycle not only provides effective climate control but also significantly reduces greenhouse gas emissions. According to the International Energy Agency, transitioning to heat pump technology could reduce global CO2 emissions from buildings by 1.6 gigatons annually by 2030, making it a key player in the pursuit of energy efficiency and sustainability in the built environment.
This bar chart demonstrates the Annual Energy Efficiency Ratio (AEER) of various heating systems. The heat pump significantly outperforms traditional systems such as gas boilers, electric furnaces, and oil furnaces, indicating its superior energy efficiency and effectiveness in energy transfer.

Energy efficient heat pumps offer significant benefits for home heating and cooling, making them an increasingly popular choice for homeowners. One of the main advantages is their ability to provide both heating and cooling from a single system, which not only simplifies maintenance but also optimizes energy use throughout the year. By transferring heat rather than generating it, these systems consume less electricity compared to traditional heating methods, leading to reduced utility bills and a smaller carbon footprint.
In addition to cost savings, energy efficient heat pumps can enhance indoor comfort. They maintain consistent temperatures and improve air quality by circulating clean, filtered air. These systems are also known for their quiet operation, contributing to a more peaceful living environment. Furthermore, many models come equipped with smart technology, allowing homeowners to adjust settings remotely and maximize energy savings. Overall, opting for energy efficient heat pumps not only promotes environmental sustainability but also elevates the comfort and efficiency of home environments.
When comparing energy usage between heat pumps and traditional heating systems, it becomes clear that heat pumps offer a more efficient solution for temperature regulation. Traditional heating systems, such as furnaces and electric resistance heaters, generate heat by burning fossil fuels or converting electricity directly into heat. This process often results in substantial energy loss, as much of the energy is transformed into heat during combustion or inefficiencies in resistance heating.
In contrast, heat pumps operate on a fundamentally different principle known as thermodynamic transfer. Instead of generating heat, they move existing heat from one location to another. During colder months, heat pumps extract heat from the outside air, ground, or water and transfer it indoors, providing warmth while consuming significantly less energy. The efficiency of heat pumps is measured by their coefficient of performance (COP), which can exceed 3.0, meaning they can produce three times more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume. As a result, households utilizing heat pumps can expect reduced energy bills and a minimized carbon footprint compared to those relying on conventional heating methods.