Leave Your Message
Choosing the best Energy Efficient Heat Pump for your home requires careful consideration. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can reduce energy consumption by 30-40% compared to traditional heating methods. This significant reduction highlights their growing role in energy conservation.
Expert Mark Johnson, a leading figure in energy solutions, states, "Selecting the right heat pump can transform your home's energy efficiency." This underscores the importance of informed decision-making. Factors such as climate, insulation, and specific needs all play a role in this choice. Many homeowners overlook the impact of proper sizing and installation, which can affect performance dramatically.
Understanding efficiency ratings, like the HSPF and SEER, is critical. These metrics help in assessing potential savings. Unfortunately, many still ignore them, leading to less efficient heating solutions. With rising energy costs, embracing an Energy Efficient Heat Pump is not just wise; it's necessary for sustainable living.
When selecting an energy-efficient heat pump, it’s essential to understand heat pump basics. A heat pump transfers heat rather than generating it. This process is more efficient than traditional heating systems. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can provide up to three times more heating energy than the electrical energy they consume.
Energy efficiency ratings play a crucial role in the selection process. Look for the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings. Higher values indicate better efficiency. For instance, a heat pump with a SEER rating over 16 and an HSPF over 9 will save energy and costs. Many households typically see a 30% reduction in energy usage when opting for higher-rated models.
Tips: Consider the size of your space. An oversized unit may lead to inefficiency, while an undersized one may struggle to heat adequately. Regular maintenance can also enhance efficiency. Skipping this step can lead to higher energy bills. Reflect on your home’s insulation. Inadequate insulation can render even the best heat pump less effective. Evaluating these factors will lead to better choices.
| Heat Pump Type | Efficiency Rating (HSPF/SEER) | Heating Capacity (BTU) | Cooling Capacity (BTU) | Estimated Annual Energy Cost ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air Source Heat Pump | 8.5 HSPF / 14 SEER | 30,000 BTU | 36,000 BTU | $1,200 |
| Geothermal Heat Pump | 14 HSPF / 22 SEER | 40,000 BTU | 42,000 BTU | $900 |
| Ductless Mini-Split Heat Pump | 9 HSPF / 18 SEER | 24,000 BTU | 30,000 BTU | $1,000 |
| Hybrid Heat Pump | 10 HSPF / 16 SEER | 35,000 BTU | 38,000 BTU | $1,150 |
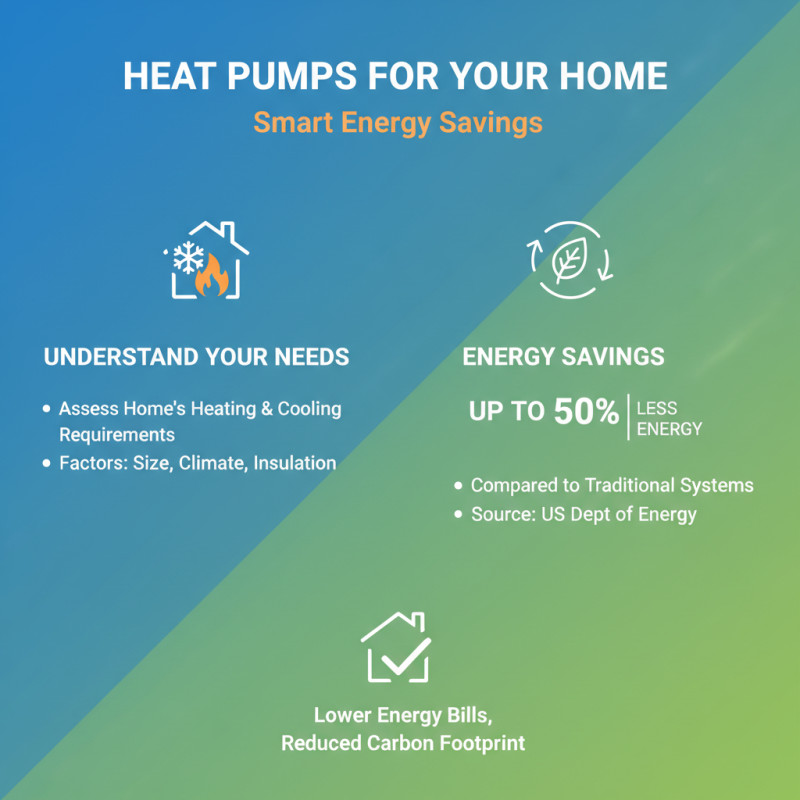
When considering a heat pump for your home, understanding your heating and cooling needs is crucial. The U.S. Department of Energy suggests that a heat pump can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% compared to traditional heating systems. However, these benefits depend on correctly assessing your home's requirements.
Start by calculating the square footage of the areas to be heated or cooled. Drafty windows and poorly insulated walls can significantly affect efficiency. In fact, the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers recommends a Manual J load calculation for precise estimates. Some homeowners overlook this step, leading to mismatched systems that either underperform or overspend on energy.
Consider local climate as well. If temperatures vary widely, a single-stage heat pump might struggle to maintain comfort. A multi-stage or variable-speed pump could be more effective but may require a higher initial investment. The trade-off, however, could be worth it if you hate constant temperature swings. Reflecting on these details is essential. Taking shortcuts in the assessment process can lead to frustration and additional costs.
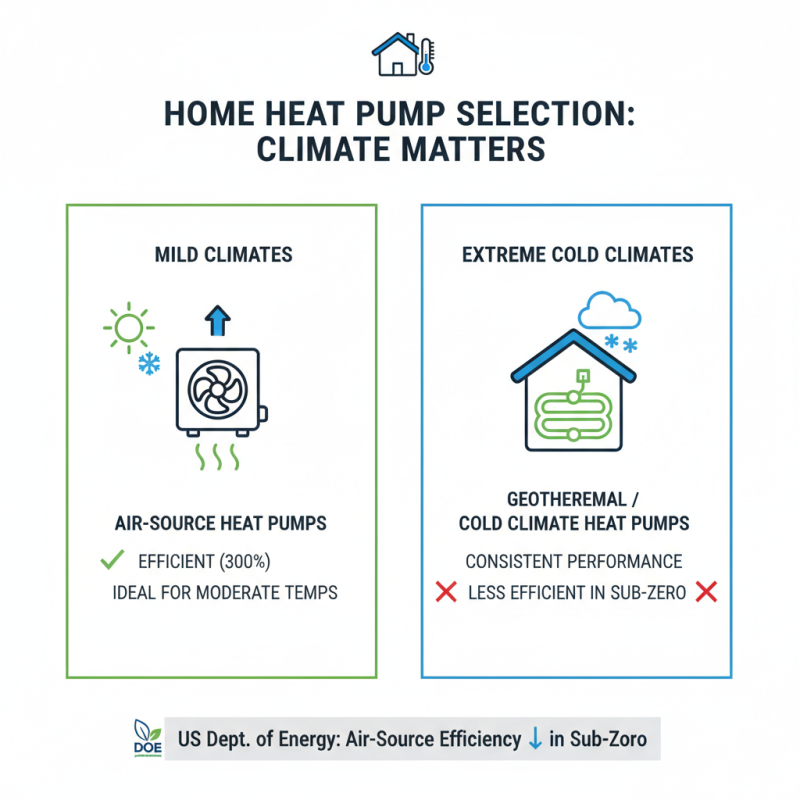
When selecting a heat pump for your home, consider your local climate. Different types of heat pumps perform uniquely depending on the weather conditions. For instance, air-source heat pumps are effective in mild climates but may struggle in extreme cold. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, air-source heat pumps can achieve efficiencies over 300%, but performance drops significantly in sub-zero temperatures.
Geothermal heat pumps provide another option. They utilize stable underground temperatures, making them efficient year-round. Studies show that they can reduce energy use for heating by 30% to 60% compared to conventional systems. However, installation costs are higher and require enough land for ground loops. This might not be feasible for all homes.
You must also consider the size. Over-sizing a heat pump can lead to short cycling, which diminishes efficiency. According to the EPA, properly sized systems can enhance comfort and save energy. Assessing your home’s insulation and layout is crucial. Even the best heat pump cannot perform well in poorly insulated spaces.
When selecting an energy-efficient heat pump, understanding the efficiency features across different brands is crucial. Many sources highlight that a heat pump with a high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) can significantly reduce electricity usage. For instance, models achieving a SEER rating of 16 or higher could yield energy savings of up to 30% compared to older models. Yet, efficiency ratings alone do not provide the complete picture.
Pay attention to the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) as well. The Department of Energy states that an HSPF of 9 or above is desirable. This translates to more efficient heating during colder months. However, not every brand offers transparent data on performance, making it essential for homeowners to do thorough research.
Consulting customer reviews and professional evaluations can provide additional insights. A sluggish heating response or inconsistent performance can indicate efficiency flaws. Some brands may outwardly claim high ratings, yet underperform in real-world situations. Therefore, comparing real-life performance data, along with efficiency features, is vital for making an informed choice.
When investing in an energy-efficient heat pump, it's crucial to consider installation costs and long-term savings. Installation can vary based on several factors, including the size of your home and specific requirements. A professional assessment can provide insights into potential costs, ensuring that you budget effectively. Always gather multiple quotes to compare.
Tips: Consider local rebates and incentives when calculating your budget. They can significantly offset initial expenses. Don't forget to check for any hidden costs associated with installation. These can add up and impact your overall savings.
Long-term savings depend on the pump's efficiency rating. Higher-rated pumps may have a larger upfront cost but can lead to substantial savings on utility bills. A well-functioning heat pump can help reduce energy usage significantly. However, you need to look beyond just the purchase price. Maintenance costs should also be part of your calculations. Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance.
Tips: Keep an eye out for energy consumption patterns after installation. If you see unusually high bills, it might indicate ineffective operation. Adjusting your usage habits can also enhance savings over time. This understanding can guide future decisions to improve efficiency.